Ultra-Thin Biocompatible Rigid-Flex Printed Circuit Board Assembly
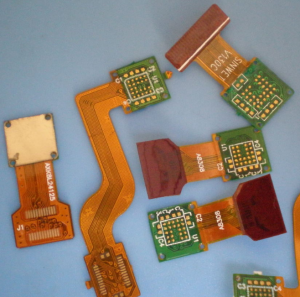
Ultra-thin biocompatible rigid-flex PCB assembly is a major breakthrough in medical technology, especially for subdermal micro-diagnostic patches.
These smart devices are changing healthcare by enabling the continuous monitoring of vital signs and diagnostic data directly under the skin.
This article explains the details of rigid-flex circuit boards and their crucial role in these advanced medical tools.
What is Rigid-Flex Circuit Board Technology?
Rigid-flex technology combines the best features of rigid and flexible circuit boards.
A rigid-flex PCB is both stable like a rigid board and can bend like a flexible one.
This allows for complex designs that fit into intricate shapes and curves, making them perfect for applications under the skin where traditional boards are too big or bulky.
The ultra-thin design is key.
Often as thin as a few micrometers, these boards can easily conform to the body’s contours, which is ideal where space is limited.
They also combine multiple functions into a single assembly, reducing the device’s size and improving comfort.
Why Biocompatibility is Essential
For any medical device used inside the body, the materials must be biocompatible—meaning they are safe, non-toxic, and won’t cause a reaction.
Ultra-thin biocompatible rigid-flex PCBs are made from lightweight, durable materials that are harmless to biological tissues.
This ensures the device remains safe and functional when implanted.
Selecting the right materials is critical.
Common choices include polyimide films and special adhesives that can withstand sterilization and perform reliably in different environments.
This ensures the diagnostic patches remain effective and long-lasting.
Enabling Subdermal Micro-Diagnostic Patches
Subdermal micro-diagnostic patches are tiny sensing devices that monitor health metrics like glucose levels, heart rate, and biochemical markers.
The use of ultra-thin biocompatible rigid-flex PCBs makes it possible to include advanced features in a very small form.
The flexibility of the PCB allows it to fit comfortably under the skin, moving naturally with the body.
This is important for long-term wear, as many health monitoring systems need to collect data continuously.
Studies show these patches greatly improve patient compliance because they avoid invasive procedures or frequent manual checks.
Additionally, these circuit boards can integrate sensors and microcontrollers for real-time data processing and wireless transmission.
Many current designs connect to smartphones and other devices, letting patients and doctors monitor health metrics easily.
This instant feedback supports better treatment decisions and lifestyle changes.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite their promise, ultra-thin biocompatible rigid-flex PCBs still face challenges.
Manufacturing is complex and expensive, requiring high precision to ensure all components work correctly.
As technology advances, the demand for even smaller and more powerful devices will continue to push innovation.
Battery life is another concern. Many micro-diagnostic patches need a power source, and optimizing energy use is essential.
Research is ongoing into solutions like energy harvesting from body movement or new battery technologies.
Conclusion
The future of healthcare is being transformed by innovations like ultra-thin biocompatible rigid-flex PCBs.
They enable the development of subdermal micro-diagnostic patches that improve patients’ quality of life and provide doctors with valuable data.
As technology evolves, these advanced materials and designs will lead to even smarter medical devices, opening a new era of personalized and proactive healthcare.
