Advancements in Rigid Flex PCB Manufacturing Technologies
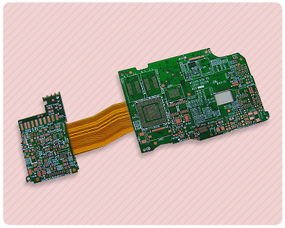
Rigid-flex PCBs have become increasingly popular in the electronics industry due to their ability to combine the benefits of both rigid and flexible PCBs in a single design. These boards are ideal for applications where space is limited, and where the board needs to be able to bend or flex without breaking.
As a result, manufacturers are constantly looking for ways to improve the manufacturing process for rigid-flex PCBs in order to meet the growing demand for these versatile boards.
One of the key advancements in rigid-flex PCB manufacturing technologies is the use of advanced materials.
Traditional rigid-flex PCBs are typically made using a combination of rigid FR4 material and flexible polyimide material.
However, manufacturers are now exploring the use of new materials such as liquid crystal polymer (LCP) and DuPont’s Pyralux material, which offer improved flexibility, thermal stability, and reliability compared to traditional materials. These advanced materials allow for more complex designs and tighter bend radii, making them ideal for applications where space is at a premium.
In addition to advanced materials, manufacturers are also investing in new manufacturing processes to improve the quality and reliability of rigid-flex PCBs. One such process is laser drilling, which allows for smaller vias and higher density interconnects compared to traditional mechanical drilling methods.
Laser drilling also produces cleaner and more precise holes, reducing the risk of shorts and opens in the final product.
Another key advancement is the use of additive manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing, to create complex shapes and features that would be difficult or impossible to achieve using traditional manufacturing methods.
Furthermore, advancements in automation and robotics have also played a significant role in improving the manufacturing process for rigid-flex PCBs. Automated assembly lines can significantly reduce the time and cost of production, while also improving the consistency and quality of the final product. Robotics can be used for tasks such as soldering, component placement, and inspection, allowing for faster and more accurate assembly of rigid-flex PCBs. These technologies not only improve efficiency but also reduce the risk of human error, resulting in higher quality and more reliable boards.
Another key advancement in rigid-flex PCB manufacturing technologies is the use of advanced design software and simulation tools.
These tools allow designers to create more complex and optimized designs, taking into account factors such as thermal management, signal integrity, and mechanical stress. By simulating the behavior of the board before production, designers can identify and address potential issues early in the design process, reducing the risk of costly rework and delays. This results in faster time-to-market and higher quality products for manufacturers.
Overall, the advancements in rigid-flex PCB manufacturing technologies have revolutionized the way these boards are designed and produced.
By using advanced materials, new manufacturing processes, automation, robotics, and design tools, manufacturers can create more complex, reliable, and cost-effective rigid-flex PCBs than ever before. As the demand for smaller, lighter, and more flexible electronics continues to grow, these advancements will play a crucial role in meeting the needs of the industry and driving innovation in the field of PCB manufacturing.
