 Benefits of Using Rigid-Flexible PCBs in Electronic Devices
Benefits of Using Rigid-Flexible PCBs in Electronic Devices
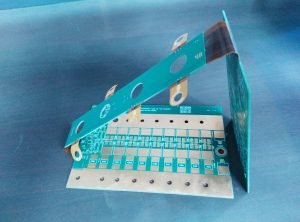
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are an essential component in electronic devices, serving as the backbone that connects various electronic components together. In recent years, there has been a growing trend towards the use of rigid-flexible PCBs in electronic devices due to their numerous benefits and applications. Rigid-flex PCBs combine the best of both rigid and flexible PCBs, offering a unique solution for electronic devices that require both flexibility and durability.
One of the key benefits of using rigid-flex PCBs is their ability to reduce the overall size and weight of electronic devices.
Traditional rigid PCBs are limited by their rigid nature, which can make it challenging to fit them into small or irregularly shaped spaces.
Flexible PCBs, on the other hand, are more versatile and can be bent or folded to fit into tight spaces. By combining rigid and flexible PCBs into
a single design, rigid-flex PCBs offer a compact and lightweight solution for electronic devices.
Another benefit of using rigid-flex PCBs is their improved reliability and durability. Traditional rigid PCBs are prone to mechanical stress and vibration, which can lead to solder joint failures and other reliability issues. Flexible PCBs, on the other hand, are more resistant to mechanical stress and vibration, making them ideal for applications where durability is a concern. Rigid-flex PCBs combine the durability of flexible PCBs with the rigidity of rigid PCBs, resulting in a more reliable and robust solution for electronic devices.
In addition to their compact size and improved reliability, rigid-flex PCBs also offer greater design flexibility. Traditional rigid PCBs are limited by their flat, two-dimensional design, which can make it challenging to design complex electronic devices. Flexible PCBs, on the other hand, can be bent or folded to create three-dimensional shapes, allowing for more creative and innovative designs. Rigid-flex PCBs combine the design flexibility of flexible PCBs with the structural integrity of rigid PCBs, offering designers the freedom to create more complex and compact electronic devices.
The applications of rigid-flex PCBs are vast and varied, spanning across a wide range of industries. One of the most common applications of rigid-flex PCBs is in the aerospace and defense industry, where they are used in avionics systems, missile guidance systems, and other critical electronic components.
The compact size and durability of rigid-flex PCBs make them ideal for use in aerospace and defense applications, where reliability and performance are paramount.
Another key application of rigid-flex PCBs is in the medical industry, where they are used in medical devices such as pacemakers, defibrillators, and medical imaging equipment. The flexibility and durability of rigid-flex PCBs make them well-suited for use in medical devices that need to withstand harsh environments and constant movement. Rigid-flex PCBs are also used in automotive electronics, consumer electronics, and industrial automation, highlighting their versatility and wide-ranging applications.
In conclusion, rigid-flex PCBs offer numerous benefits and applications in the electronic industry. From their compact size and improved reliability to their greater design flexibility, rigid-flex PCBs provide a unique solution for electronic devices that require both flexibility and durability. As the demand for smaller, more reliable electronic devices continues to grow, rigid-flex PCBs are poised to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of electronic design and manufacturing.
