Manufacturing Considerations in Rigid-Flex PCB Design: A Step-by-Step Guide
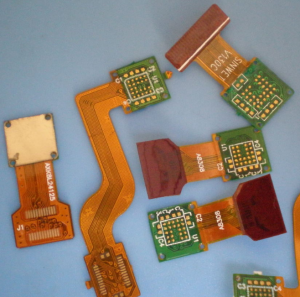
Manufacturing considerations in rigid-flex PCB design are crucial for ensuring the success of your electronic products.
Rigid-flex PCBs combine the advantages of both rigid and flexible circuits, making them an optimal choice for applications where space is at a premium or where dynamic movement is required.
However, designing these boards is not a straightforward process; it involves a series of meticulous decisions that can significantly affect manufacturability, reliability, and overall performance.
Understanding Rigid-Flex PCB Design
Before diving deep into manufacturing considerations, it’s essential to understand what rigid-flex PCBs entail.
These boards consist of both rigid and flexible substrates, allowing designers to create complex circuit patterns that can bend and flex.
Their applications range from medical devices and aerospace technologies to consumer electronics.
Step 1: Define Your Requirements
The first step in the design process is to clearly define your product requirements. This includes:
- Size and Shape: What dimensions must the PCB fit within?
- Layer Count: How many layers will your design require?
- Material Selection: What materials best suit your application? For instance, materials with high thermal stability might be necessary for high-performance electronics.
Step 2: Consider Mechanical Forces
Mechanical forces during manufacturing and operation can seriously impact the integrity of rigid-flex PCBs. Therefore, it is vital to:
- Analyze Stress Points: Identify areas where the PCB may experience bending or twisting. Make sure to design around these points.
- Choose the Right Thickness: Using thinner materials can provide flexibility, but ensure they can withstand the required stress.
Step 3: Layer Configuration
The layer configuration plays a significant role in how well the PCB performs. Consider the following:
- Bonding Technologies: Different bonding methods (e.g., adhesive, controlled peel, etc.) will impact electrical performance and reliability.
- Layer Alignment: Ensure that all layers are properly aligned during manufacturing to avoid issues such as shorts and reduced performance.
Step 4: Electrical Considerations
When dealing with rigid-flex PCBs, electrical considerations can often be more complex than in traditional designs. Some recommendations include:
- Impedance Control: Maintain controlled impedance to reduce signal reflection and loss.
- Grounding and Shielding: Add adequate grounding and shielding to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Step 5: Fabrication Techniques
The fabrication técnicas used in rigid-flex PCB manufacturing can greatly influence the final product’s quality and reliability. Key considerations should include:
- Drilling and Routing: These processes should be done precisely to avoid creating stress points that could impact reliability.
- Via Design: Blind and buried vias might be necessary for complicated designs, but consider the impact of via size and placement on manufacturability.
Step 6: Testing and Validation
Once the PCB has been manufactured, rigorous testing and validation are essential to ensure it meets all performance requirements. Procedures should include:
- Mechanical Testing: Assess flexural strength and other mechanical properties under operational conditions.
- Electrical Testing: Perform continuity testing and signal integrity analysis to ensure the board is functioning correctly.
Step 7: Collaboration with Manufacturers
Finally, continuous collaboration with your PCB manufacturer during the design phase can save time and money. By engaging in open dialogue, you can:
- Receive Feedback on Design: Manufacturers can offer valuable insights into which design features may pose challenges.
- Adjust to Manufacturing Capabilities: Ensure your design aligns with the capabilities and limitations of the manufacturer’s processes.
Conclusion
Manufacturing considerations in rigid-flex PCB design are multifaceted and require a comprehensive approach to ensure a successful outcome.
By defining your requirements, understanding mechanical forces, selecting the right layer configuration, considering electrical properties, and collaborating with manufacturers throughout the process, you can drive your design toward success. With careful attention to these steps, your rigid-flex PCB can deliver the advanced functionality needed for today’s demanding applications.
