Advancements in Rigid-Flexible PCB Manufacturing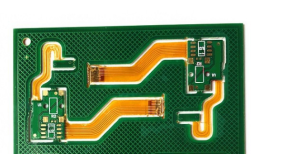
In recent years, there have been significant advancements in the field of rigid-flexible PCB manufacturing and surface mount technology (SMT) assembly.
These innovations have revolutionized the way electronic devices are designed and manufactured, leading to more compact, lightweight, and reliable products. In this article, we will explore some of the key developments in this area and their implications for the electronics industry.
One of the most notable advancements in rigid-flexible PCB manufacturing is the use of advanced materials and manufacturing techniques.
Traditional rigid PCBs are made of rigid materials such as FR4, while flexible PCBs are made of flexible materials such as polyimide. However, with the advent of rigid-flex PCBs, manufacturers can now combine both rigid and flexible materials in a single board, allowing for greater design flexibility and improved reliability.
Another key innovation in rigid-flexible PCB manufacturing is the use of additive manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing.
This technology allows for the rapid prototyping and production of complex PCB designs, reducing time-to-market and overall manufacturing costs. Additionally, 3D printing enables the creation of intricate geometries and structures that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods.
In addition to advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques, there have been significant improvements in SMT assembly processes for rigid-flexible PCBs. SMT assembly is a critical step in the manufacturing process, where electronic components are mounted onto the PCB using solder paste and reflow soldering. With the increasing complexity and miniaturization of electronic devices, precise and reliable SMT assembly is more important than ever.
One of the key innovations in SMT assembly for rigid-flexible PCBs is the use of advanced pick-and-place machines and automated assembly systems.
These machines are capable of placing components with micron-level precision, ensuring optimal electrical connections and reliability. Additionally, automated assembly systems can significantly increase production throughput and efficiency, reducing labor costs and improving overall product quality.
Furthermore, advancements in soldering technologies have also played a crucial role in improving SMT assembly for rigid-flexible PCBs. Lead-free solder alloys, such as SAC305, have become increasingly popular due to their environmental benefits and improved mechanical properties. Additionally, the development of reflow soldering techniques, such as vapor phase soldering and infrared reflow, has enabled manufacturers to achieve more consistent and reliable solder joints.
Overall, the combination of innovations in rigid-flexible PCB manufacturing and SMT assembly has led to significant improvements in the design, production, and reliability of electronic devices. These advancements have enabled manufacturers to create more compact and lightweight products, while also improving performance and durability. As the electronics industry continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more exciting developments in rigid-flexible PCB manufacturing and SMT assembly, further pushing the boundaries of what is possible in electronic design and manufacturing.
