Flexible Manufacturing: The production of rigid flex PCBs can be adapted to various manufacturing processes, accommodating different volumes and designs
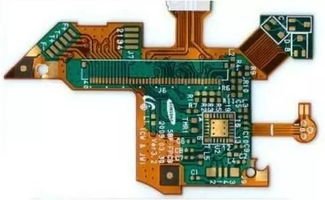
The production of rigid-flex printed circuit boards (PCBs) is a highly adaptable process, capable of accommodating a wide range of manufacturing requirements, from low-volume prototypes to high-volume mass production. This flexibility makes rigid-flex PCBs an ideal choice for industries with diverse needs, enabling manufacturers to efficiently produce customized designs while maintaining high quality and cost-effectiveness. The ability to adapt to various manufacturing processes is one of the key reasons rigid-flex PCBs are increasingly favored in today’s fast-paced electronics industry.
One of the standout features of rigid-flex PCB manufacturing is its compatibility with both small-scale and large-scale production. For startups and research institutions working on prototypes or specialized projects, rigid-flex PCBs can be produced in low volumes without incurring excessive costs. This allows designers to test and refine their concepts before committing to full-scale production. On the other hand, for industries like consumer electronics, automotive, and aerospace, where high-volume production is essential, rigid-flex PCBs can be manufactured at scale with consistent quality and precision. This versatility ensures that rigid-flex PCBs can meet the needs of virtually any application.
The manufacturing process for rigid-flex PCBs is also highly adaptable to different design requirements. Whether the application demands a compact, lightweight board for a wearable device or a robust, multi-layered board for an aerospace system, the production process can be tailored to meet these specific needs. Advanced manufacturing techniques, such as laser drilling, precision etching, and automated assembly, enable the creation of complex designs with high accuracy. This adaptability is particularly valuable in industries like medical devices and IoT, where custom solutions are often required to meet unique performance and form factor requirements.
Another advantage of flexible manufacturing is the ability to integrate new materials and technologies into the production process. For example, manufacturers can use high-performance materials with enhanced thermal or electrical properties to meet the demands of high-frequency or high-temperature applications. Additionally, advancements in additive manufacturing and 3D printing are opening up new possibilities for creating rigid-flex PCBs with even greater precision and customization.
The flexibility of rigid-flex PCB manufacturing also extends to post-production processes, such as testing and quality control. Rigid-flex PCBs can be designed with built-in test points and features that simplify the inspection process, ensuring that each board meets the required standards. This is particularly important in industries like aerospace and medical devices, where reliability is critical. By incorporating testing into the manufacturing process, manufacturers can identify and address potential issues early, reducing waste and improving overall efficiency.
Furthermore, the ability to adapt to changing market demands is a significant advantage of flexible manufacturing. As technology evolves and new trends emerge, manufacturers can quickly adjust their processes to accommodate new designs or materials. This agility is essential in industries like consumer electronics, where product lifecycles are short, and innovation is constant.
In conclusion, the flexible manufacturing of rigid-flex PCBs enables manufacturers to meet a wide range of production needs, from low-volume prototypes to high-volume mass production. By adapting to different designs, materials, and technologies, rigid-flex PCBs provide a versatile and cost-effective solution for industries with diverse requirements. As the demand for customized and high-performance electronics continues to grow, the flexibility of rigid-flex PCB manufacturing will remain a key driver of innovation and efficiency in the electronics industry.
