Flex PCB vs Rigid Flex PCB: Which is the Right Choice for Your Application?
Flex PCB vs Rigid Flex PCB: Which is the Right Choice for Your Application?
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are an essential component in many electronic devices, providing a platform for connecting and supporting various electronic components.
When it comes to PCB design, there are two main types to consider: flex PCBs and rigid flex PCBs.
Both offer unique advantages and are suitable for different applications.
In this article, we will explore the differences between flex PCBs and rigid flex PCBs to help you determine which is the right choice for your specific application.
Flex PCBs, as the name suggests, are flexible circuit boards that can bend and twist to fit into tight spaces or conform to the shape of the device they are installed in.
These boards are made of a thin, flexible substrate material, such as polyimide, that allows for greater design flexibility compared to traditional rigid PCBs.
Flex PCBs are ideal for applications where space is limited or where the board needs to be bent or folded to fit into a specific form factor.
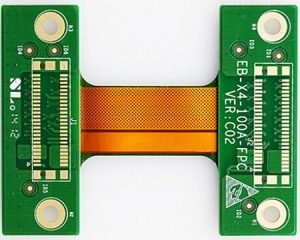
On the other hand, rigid flex PCBs combine the benefits of both rigid and flex PCBs by incorporating both rigid and flexible sections into a single board.
This allows for greater design flexibility while still providing the structural stability of a rigid board. Rigid flex PCBs are ideal for applications that require a combination of flexibility and durability, such as in aerospace, medical devices, or automotive electronics.
One of the main differences between flex PCBs and rigid flex PCBs is their construction.
Flex PCBs are typically made of a single layer of flexible substrate material, while rigid flex PCBs consist of multiple layers of both rigid and flexible materials. This difference in construction affects the overall flexibility and durability of the board, as well as the complexity of the design.
In terms of cost, flex PCBs are generally more affordable than rigid flex PCBs due to their simpler construction and lower material costs.
However, the cost of each type of PCB can vary depending on the specific design requirements and manufacturing processes involved.
It is important to consider both the upfront cost and long-term benefits of each type of PCB when making a decision for your application.
When it comes to performance, both flex PCBs and rigid flex PCBs offer similar electrical characteristics and reliability.
However, rigid flex PCBs are generally more robust and resistant to mechanical stress, making them ideal for applications that require a higher level of durability.
Flex PCBs, on the other hand, are more flexible and can be bent or folded without compromising their performance, making them suitable for applications where flexibility is a key requirement.
In conclusion, the choice between flex PCBs and rigid flex PCBs ultimately depends on the specific requirements of your application.
If you need a flexible board that can bend and twist to fit into tight spaces, a flex PCB may be the right choice for you.
On the other hand, if you require a board that offers a combination of flexibility and durability, a rigid flex PCB may be more suitable.
Consider factors such as cost, performance, and design requirements when making your decision, and consult with a PCB manufacturer to determine the best option for your application.
