Benefits of Miniaturized Rigid-Flex PCBs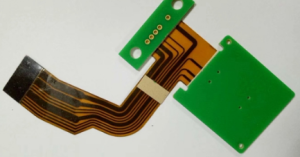
Miniaturized rigid-flex PCBs have become increasingly popular in the electronics industry due to their numerous benefits.
These compact circuit boards offer a combination of rigid and flexible sections, allowing for greater design flexibility and space-saving capabilities.
When designing miniaturized rigid-flex PCBs, there are several key considerations that must be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
One of the primary benefits of miniaturized rigid-flex PCBs is their ability to reduce overall size and weight in electronic devices.
By combining rigid and flexible sections in a single board, designers can create compact and lightweight solutions for a wide range of applications.
This is particularly advantageous in portable devices where space is limited and weight must be minimized.
In addition to size and weight savings, miniaturized rigid-flex PCBs offer improved reliability compared to traditional rigid PCBs.
The flexible sections of the board help to absorb mechanical stresses and vibrations, reducing the risk of component failure due to bending or flexing.
This is especially important in applications where the PCB may be subjected to repeated bending or movement.
Another key benefit of miniaturized rigid-flex PCBs is their ability to simplify assembly and reduce the number of interconnects required.
By integrating multiple rigid and flexible sections into a single board, designers can eliminate the need for complex wiring harnesses and connectors,
streamlining the assembly process and reducing the risk of connection errors. This can result in cost savings and improved overall product quality.
When designing miniaturized rigid-flex PCBs, it is important to consider the specific requirements of the application and the environment in which the board will be used.
Factors such as temperature, humidity, and mechanical stresses must be taken into account to ensure that the board will perform reliably under all conditions.
Special attention must also be paid to the materials used in the construction of the board, as different materials offer varying levels of flexibility and durability.
In addition to environmental considerations, designers must also pay close attention to signal integrity and electrical performance when designing miniaturized rigid-flex PCBs.
The compact nature of these boards can present challenges in terms of signal routing and impedance control, which can impact the overall performance of the circuit.
Careful planning and simulation are essential to ensure that the board meets the required electrical specifications and performance criteria.
Overall, miniaturized rigid-flex PCBs offer a wide range of benefits for electronic device manufacturers, including size and weight savings, improved reliability, simplified assembly, and enhanced electrical performance.
By carefully considering the design requirements and constraints of the application, designers can create miniaturized rigid-flex PCBs that meet the specific needs of their customers and deliver high-quality, reliable solutions for a variety of applications.
