Advanced Materials Used in Rigid Flex PCB Manufacturing
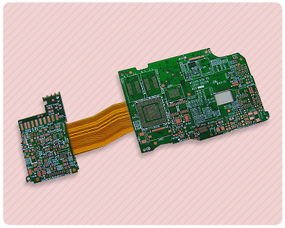
Rigid-flex PCBs have become increasingly popular in the electronics industry due to their ability to combine the benefits of both rigid and flexible PCBs.
These boards are made up of a combination of rigid and flexible materials, allowing for greater design flexibility and reliability.
In order to manufacture these advanced PCBs, cutting-edge materials and techniques are required.
One of the key materials used in rigid-flex PCB manufacturing is polyimide.
Polyimide is a high-performance polymer that is known for its excellent thermal stability and mechanical properties.
It is used as the flexible substrate in rigid-flex PCBs, providing the flexibility needed for the board to bend and twist without breaking.
Polyimide also has a high glass transition temperature, making it ideal for applications that require high temperatures.
Another important material used in rigid-flex PCB manufacturing is copper.
Copper is used as the conductive material in the PCB, providing the electrical connections between components.
Copper is preferred for its high conductivity and excellent solderability, making it an ideal choice for high-performance applications.
In rigid-flex PCBs, copper is typically plated onto the polyimide substrate using a process called electroplating.
In addition to polyimide and copper, other materials such as solder mask and coverlay are also used in rigid-flex PCB manufacturing.
Solder mask is a protective layer that is applied over the copper traces to prevent short circuits and corrosion.
Coverlay, on the other hand, is a flexible adhesive film that is used to encapsulate the flexible portions of the PCB, providing protection and insulation.
To manufacture rigid-flex PCBs, advanced techniques such as laser drilling and sequential lamination are used.
Laser drilling is a precise and efficient method of creating vias in the PCB, allowing for the electrical connections to be made between layers.
This technique is especially important in rigid-flex PCBs, where the layers need to be connected in both the rigid and flexible portions of the board.
Sequential lamination is another key technique used in rigid-flex PCB manufacturing.
This process involves laminating multiple layers of materials together in a specific sequence to create the final PCB. By carefully controlling the lamination process, manufacturers can ensure that the layers are properly aligned and bonded together, resulting in a high-quality and reliable PCB.
Overall, the materials and techniques used in rigid-flex PCB manufacturing play a crucial role in the performance and reliability of the final product.
By using advanced materials such as polyimide and copper, and employing techniques like laser drilling and sequential lamination, manufacturers can create cutting-edge rigid-flex PCBs that meet the demands of today’s high-tech applications.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative materials and techniques being used in the manufacturing of rigid-flex PCBs, further pushing the boundaries of what is possible in electronics design.
