Balancing Performance and Cost in Rigid-Flex PCB Design
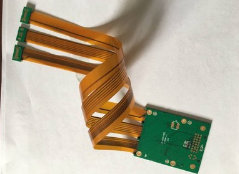
Balancing performance and cost in rigid-flex PCB design can be a challenging endeavor for engineers and manufacturers alike.
Rigid-flex printed circuit boards (PCBs) have gained popularity across various industries due to their versatility and compactness.
However, maximizing performance while keeping costs in check requires a thoughtful approach to design and manufacturing processes.
This article delves into the key factors to consider in order to strike the right balance in rigid-flex PCB design.
Understanding Rigid-Flex PCBs
Rigid-flex PCBs combine the best features of both rigid and flexible circuit boards.
These hybrid boards allow for more intricate designs and optimized performance in compact spaces.
By integrating rigid and flexible sections, manufacturers can create products that meet unique requirements, such as lightweight constructions and improved connectivity.
This innovative design is ideal for applications in industries like telecommunications, medical devices, aerospace, and consumer electronics.
Key Considerations for Performance Optimization
When designing rigid-flex PCBs, prioritizing performance without overspending involves several considerations:
1. Material Selection
Choosing the right materials is essential for both cost-effectiveness and performance.
High-quality materials such as polyimide for flexible sections and FR-4 for rigid areas can significantly influence signal integrity, durability, and overall reliability.
While premium materials often come at a higher price, they may offer advantages in specific applications that justify the investment.
Consider long-term performance needs to select materials that meet both functionality and budget requirements.
2. Layer Stack-Up Configuration
A well-optimized layer stack-up is crucial for achieving desired electrical performance.
Properly configuring the number of layers and their arrangement affects impedance control, heat distribution, and signal integrity.
A thorough analysis of the design’s electrical requirements and performance goals will guide decisions on the appropriate stack-up configuration while considering cost implications from additional layers.
Cost-Effective Design Techniques
To balance performance with budget constraints, there are several cost-effective design techniques that can be adopted:
1. Minimizing Layer Count
Every additional layer in a PCB design can significantly increase manufacturing costs.
By streamlining designs to minimize layers while still meeting performance specifications, designers can keep expenses in check.
This may require innovative routing and thoughtful layout techniques to ensure that the PCB functions effectively with fewer layers.
2. Simplifying Geometry
Intricate geometries may enhance the performance of a circuit but can also lead to higher production costs.
Simplifying the design by reducing the complexity of shapes, pad sizes, or routing density can lead to cost savings.
However, it’s important to remain mindful of performance benchmarks and not compromise essential functionalities for the sake of cost reduction.
Collaboration with Manufacturers
Collaboration with experienced manufacturers is vital in balancing performance and costs effectively.
They can provide valuable insights into the capabilities and limitations of various materials and techniques.
Early engagement with manufacturers can lead to design optimizations that enhance performance while identifying cost-saving opportunities.
1. Prototyping and Testing
Investing in prototypes offers the chance to test designs in real-world conditions, providing crucial data on performance.
This step may reveal areas for cost reductions, such as material adjustments or design alterations that do not compromise functionality.
Early-stage prototyping can help tune performance parameters, potentially leading to significant savings in the final production run.
Conclusion
In the realm of rigid-flex PCB design, striking the right balance between performance and cost is imperative for successful product development.
By selecting the appropriate materials, optimizing layer configurations, adopting cost-effective design strategies, and collaborating closely with manufacturers, engineers can create superior rigid-flex PCBs without breaking the bank. This careful balancing act, tailored to specific project needs, will ultimately lead to innovative solutions that satisfy both technical and budgetary requirements in a competitive marketplace.
