Advanced Rigid-Flex PCB Design Techniques for Aerospace and Medical Devices
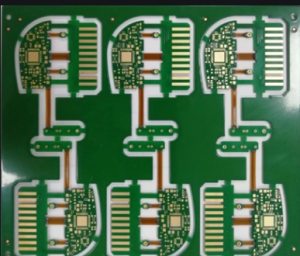
Advanced rigid-flex PCB design techniques are critical in meeting the stringent requirements of both aerospace and medical devices.
As technology continually evolves, the need for flexibility, miniaturization, and enhanced reliability in printed circuit boards (PCBs) becomes paramount.
This article explores various state-of-the-art rigid-flex PCB design methodologies tailored for aerospace and medical applications, where performance and safety are non-negotiable.
Understanding Rigid-Flex PCBs
Rigid-flex PCBs combine the best features of rigid and flexible circuits, allowing engineers to create compact and complex designs that can withstand harsh environments.
These boards are made up of multiple layers where some layers are rigid while others are flexible, enabling intricate routing options and compact packaging.
This unique design approach is especially beneficial in applications where space is at a premium, such as in aerospace and medical devices.
Importance of Advanced Design Techniques
When designing rigid-flex PCBs for aerospace and medical devices, several advanced techniques come into play:
- Layer Stacking Optimization
Layer stacking is crucial for achieving the desired electrical performance.
By optimizing the number of layers and their arrangement, engineers can enhance signal integrity, reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI), and improve thermal management.
Utilizing high-frequency laminates for the outer layers can significantly improve performance while maintaining a compact design. - Design for Manufacturing (DFM)
Incorporating DFM principles allows designers to anticipate potential hurdles during production.
This involves proper spacing, hole sizes, and interconnections to minimize defects.
For rigid-flex PCBs, ensuring that the flexible areas bend without damaging the circuit is crucial, and this necessitates careful design considerations. - Thermal Management Techniques
In aerospace and medical applications, devices often operate under diverse and extreme temperature conditions.
Advanced thermal management strategies like thermal vias and copper planes help dissipate heat effectively.
These techniques enhance the reliability and longevity of the PCBs, which is essential in mission-critical environments.
Challenges in Rigid-Flex PCB Design
While advanced techniques provide significant advantages, they also come with inherent challenges:
- Complexity of Layout
The combination of rigid and flexible layers can make the design immensely complex.
Designers must be skilled at integrating the two types seamlessly while ensuring that all connections remain intact through various bending scenarios. - Material Selection
The materials chosen for rigid-flex PCBs have a significant impact on the final product’s performance.
In aerospace, materials must be lightweight with high thermal stability, while in medical devices, biocompatible materials are often required. This necessitates extensive research and material testing.
Best Practices for Rigid-Flex PCB Design
To successfully implement advanced rigid-flex PCB designs in aerospace and medical devices, consider the following best practices:
- Comprehensive Simulation
Simulation tools are invaluable in predicting how the PCB will interact with external factors.
By utilizing electromagnetic simulation software, engineers can visualize signal integrity and couple effects, which helps in making informed design decisions. - Prototyping and Testing
Building prototypes is essential to validate the design. Real-world testing efficiently identifies issues not anticipated during the design phase.
Iterative testing allows for refinements to achieve optimal performance. - Collaboration with Manufacturers
Close collaboration between engineers and manufacturers is vital.
Developers should engage with PCB manufacturers early in the design process to leverage their expertise and insights, which can lead to enhancements in the final product.
Future Trends in Rigid-Flex PCB Design
The landscape of rigid-flex PCB design is rapidly evolving, particularly in aerospace and medical sectors.
Emerging trends include:
- Integration with IoT
As the Internet of Things (IoT) becomes more prevalent, the demand for connected medical devices and aerospace systems rises.
Rigid-flex PCBs will play a crucial role in facilitating seamless communication between these devices. - Sustainability
Environmental considerations are becoming more prominent.
Future designs may prioritize materials that are more eco-friendly while maintaining performance.
Sustainable practices throughout the manufacturing process can also reduce the carbon footprint.
Conclusion
Advanced rigid-flex PCB design techniques are indispensable for meeting the intricate demands of aerospace and medical devices.
By leveraging innovative approaches and materials, engineers can create highly efficient, reliable, and compact PCBs that stand the test of time.
As technology evolves, continuous learning and adaptation will be key in driving advancements in the industry, ensuring that the devices we rely on are not only state-of-the-art but also safe and reliable.
