Top 10 Rigid-Flex PCB Design Guidelines for Reliable Circuits
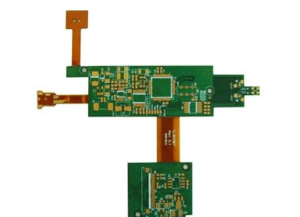
Rigid-flex PCBs have gained popularity due to their unique combination of flexibility and stability.
This fusion allows for innovative designs that can be compact and lightweight while remaining robust.
As industries increasingly adopt this technology, understanding the design guidelines for rigid-flex PCBs becomes essential for ensuring reliable circuits.
In this article, we will explore ten crucial design guidelines that every engineer should consider in their layouts.
1. Understand the Application Requirements
Before diving into the design, it’s vital to grasp the specific needs of the application.
Different projects may have varying constraints like size, weight, and environmental factors. Clearly defining these requirements will help in making design decisions that prioritize reliability.
2. Choose the Right Materials
Material selection plays a crucial role in the performance of rigid-flex PCBs.
Common materials include polyimide for the flexible sections and FR-4 for the rigid parts.
It’s essential to consider factors such as thermal stability, dielectric properties, and mechanical strength when choosing materials.
Using high-quality materials can enhance durability and performance, which are critical for long-term reliability.
3. Design for Flexibility
When designing for flexibility, ensure that bends and flex areas are strategically positioned away from rigid components.
Utilize controlled impedance traces and avoid sharp corners, as these can lead to cracking or delamination over time.
Integrate design features that allow for smooth transitions between rigid and flexible areas, ensuring the PCB can withstand repeated bending without compromising functionality.
4. Circuit and Layer Stack-Up
Establishing the right layer stack-up is foundational for achieving the desired performance in rigid-flex PCBs.
Typically, the stack-up will include alternating layers of rigid and flexible materials.
Aim for a balanced layer count to ensure even thermal distribution and electrical performance.
Proper stack-up also helps in signal integrity management.
5. Maintain Design Rule Constraints
Adhering to strict design rules is crucial for producing reliable circuits.
Keep trace widths, spacing, and drill sizes within the recommended guidelines.
Following industry-standard design rules will help avoid manufacturing issues and ensure the final product meets performance expectations.
6. Use Inspection and Testing Points
Incorporating inspection and testing points into your design can significantly improve reliability.
These points allow for easy access during manufacturing and enable engineers to troubleshoot issues more effectively.
They can also facilitate quicker testing and validation of circuits before full-scale production.
7. Thermal Management Considerations
Rigorous thermal management is essential in rigid-flex PCB designs, particularly in high-power applications.
Utilize copper pours or thermal vias to promote heat dissipation across the board.
This ensures that the components remain within operational temperature limits, preventing failures or performance degradation over time.
8. Plan for Assembly
Both design and assembly processes need to be coordinated to achieve optimal results.
Simplifying assembly by minimizing layer count and avoiding overly complex components can lead to more efficient manufacturing.
Engage with your PCB fabricator and assembler early in the design process to ensure that your design is suited for production capabilities.
9. Simulate for Reliability
Simulation tools are invaluable for predicting how a rigid-flex PCB will perform under various conditions.
Utilize simulation software to identify weak points in your design, such as stress concentrations or impedance mismatches.
Running simulations early in the design phase can save time and cost by catching potential issues before fabrication.
10. Validate Through Prototyping
Finally, prototyping should never be overlooked. Creating a prototype allows you to test the physical characteristics and electrical performance of the design in real-world conditions.
This step is critical for validating that the design meets all specifications and reliability standards before mass production.
Conduct thorough testing, including environmental and stress tests, to ensure the circuit performs as intended.
Conclusion
By adhering to these ten guidelines, designers can create rigid-flex PCBs that are not only innovative but also reliable.
Understanding the intricacies of material selection, circuit design, thermal management, and assembly processes is key to achieving success in any project.
As the demand for flexible and compact electronics rises, knowledge of these principles will position engineers to harness the full potential of rigid-flex PCB technology, leading to better, more resilient devices.
