Benefits of Using Rigid Flex PCBs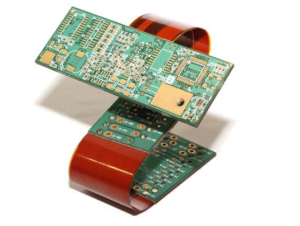
Rigid-flex PCBs, or printed circuit boards, have become increasingly popular in the electronics industry due to their numerous benefits and advantages over traditional rigid PCBs. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the benefits of using rigid-flex PCBs in various applications.
One of the primary benefits of using rigid-flex PCBs is their flexibility and versatility. Unlike rigid PCBs, which are limited in terms of shape and size, rigid-flex PCBs can be bent, folded, or twisted to fit into tight spaces or odd-shaped enclosures. This flexibility allows for more compact and lightweight designs, making them ideal for applications where space is limited or where weight reduction is critical.
Another key benefit of rigid-flex PCBs is their reliability and durability. The flexible portion of the PCB is made of polyimide, a highly durable and heat-resistant material that can withstand harsh environmental conditions, such as high temperatures, humidity, and vibration. This makes rigid-flex PCBs ideal for applications that require high reliability and long-term performance, such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices.
In addition to their flexibility and reliability, rigid-flex PCBs offer improved signal integrity and reduced electromagnetic interference (EMI).
The flexible portion of the PCB acts as a shield, protecting sensitive components from external interference and minimizing signal loss.
This results in better performance and higher data transmission rates, making rigid-flex PCBs ideal for high-speed and high-frequency applications,
such as telecommunications, networking, and data storage.
Furthermore, rigid-flex PCBs are cost-effective and time-saving compared to traditional rigid PCBs with separate connectors and cables.
By integrating the flexible portion of the PCB directly into the design, manufacturers can reduce the number of components, assembly steps,
and potential points of failure, resulting in lower production costs and faster time-to-market. This makes rigid-flex PCBs a cost-effective solution
for mass production and high-volume applications.
Moreover, rigid-flex PCBs offer improved thermal management and heat dissipation compared to traditional rigid PCBs.
The flexible portion of the PCB acts as a heat sink, dissipating heat away from sensitive components and reducing the risk of overheating.
This is particularly important for applications that require high power densities or operate in extreme temperature environments, such as industrial automation, power electronics, and LED lighting.
In conclusion, rigid-flex PCBs offer a wide range of benefits and advantages over traditional rigid PCBs, including flexibility, reliability, signal integrity, EMI protection, cost-effectiveness, time-saving, thermal management, and heat dissipation. These benefits make rigid-flex PCBs an ideal choice for a variety of applications in the electronics industry, from consumer electronics and wearable devices to automotive and aerospace systems. As technology continues to evolve and demand for smaller, lighter, and more reliable electronic devices grows, rigid-flex PCBs are expected to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of electronics design and manufacturing.
