Benefits of Using Rigid Flex PCBs in Electronic Devices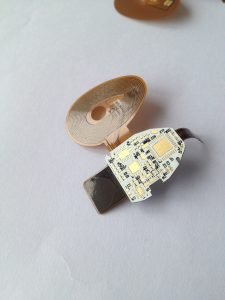
In the ever-evolving world of electronics, the demand for smaller, more compact devices continues to grow.
As technology advances, consumers expect their electronic devices to become increasingly portable and lightweight.
This trend has led to the development of rigid flex PCBs, a key component in achieving miniaturization in electronic devices.
Rigid flex PCBs, or rigid-flexible printed circuit boards, combine the benefits of both rigid and flexible PCBs into a single unit.
These boards consist of multiple layers of flexible circuit substrates attached to one or more rigid boards.
This unique construction allows for greater design flexibility and the ability to create complex, three-dimensional shapes that would be impossible with traditional rigid PCBs.
One of the primary benefits of using rigid flex PCBs in electronic devices is their ability to reduce the overall size and weight of the device.
By eliminating the need for bulky connectors and cables, rigid flex PCBs enable designers to create more compact and lightweight devices.
This is particularly important in industries such as aerospace, medical, and automotive, where space is at a premium and every millimeter counts.
Another advantage of rigid flex PCBs is their reliability and durability.
The flexible circuit substrates are designed to withstand bending and flexing without compromising the integrity of the circuitry.
This makes rigid flex PCBs ideal for applications that require frequent movement or exposure to harsh environments.
Additionally, the elimination of connectors and cables reduces the risk of mechanical failure, improving the overall reliability of the device.
In addition to their compact size and reliability, rigid flex PCBs offer improved signal integrity and reduced electromagnetic interference.
The close proximity of the flexible circuit substrates to the rigid boards minimizes signal loss and crosstalk, resulting in better performance and higher data transfer speeds. This is especially important in high-speed applications such as telecommunications, where signal integrity is critical.
Furthermore, rigid flex PCBs are cost-effective in the long run.
While the initial manufacturing costs may be higher than traditional rigid PCBs, the savings in assembly time, materials, and maintenance can offset these costs over time. Additionally, the reduced size and weight of the device can lead to lower shipping and handling costs, further increasing the overall cost-effectiveness of using rigid flex PCBs.
Overall, the benefits of using rigid flex PCBs in electronic devices are clear.
From their ability to reduce size and weight, to their reliability, signal integrity, and cost-effectiveness, rigid flex PCBs are a key component in achieving miniaturization in electronic devices. As technology continues to advance and consumer demand for smaller, more portable devices grows, rigid flex PCBs will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of electronics.
