Flex PCB vs Rigid Flex PCB: Future Trends and Innovations in Flexible Electronics
Flexible electronics have been gaining popularity in recent years due to their ability to conform to various shapes and sizes, making them ideal for a wide range of applications.
Two common types of flexible circuit boards are flex PCBs and rigid flex PCBs. While both serve similar purposes, there are key differences between the two that can impact their performance and applications.
Flex PCBs, also known as flexible printed circuit boards, are made of a flexible substrate material such as polyimide or polyester.
These materials allow the PCB to bend and twist without breaking, making them ideal for applications where space is limited or where the PCB needs to conform to a specific shape. Flex PCBs are commonly used in devices such as smartphones, wearables, and medical devices.
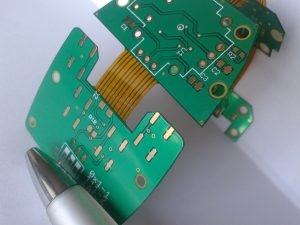
On the other hand, rigid flex PCBs combine the flexibility of a flex PCB with the rigidity of a traditional PCB.
These boards consist of multiple layers of flexible and rigid materials that are interconnected to create a single, integrated circuit board.
Rigid flex PCBs are often used in applications where the PCB needs to be both flexible and durable, such as in aerospace, automotive, and military applications.
One of the main advantages of flex PCBs is their ability to reduce the size and weight of electronic devices.
By using a flexible substrate material, designers can create PCBs that can be folded or bent to fit into tight spaces, allowing for more compact and lightweight devices.
This is especially important in applications where size and weight are critical factors, such as in wearable technology or IoT devices.
Rigid flex PCBs, on the other hand, offer the best of both worlds by combining the flexibility of a flex PCB with the durability of a rigid PCB.
This allows for more complex and reliable designs that can withstand harsh environments and high levels of vibration.
Rigid flex PCBs are often used in applications where reliability and durability are paramount, such as in automotive electronics or aerospace systems.
In terms of cost, flex PCBs are generally more affordable than rigid flex PCBs due to their simpler construction and fewer materials.
However, the cost of flex PCBs can vary depending on the complexity of the design and the materials used.
Rigid flex PCBs, on the other hand, are more expensive due to their complex construction and the use of multiple materials.
However, the durability and reliability of rigid flex PCBs often justify the higher cost, especially in high-risk applications.
Looking towards the future, the trend in flexible electronics is towards even more innovative and advanced designs.
One of the key areas of focus is on improving the flexibility and durability of flexible circuit boards to expand their applications in a wider range of industries. Researchers are also exploring new materials and manufacturing techniques to create flexible electronics that are more efficient, reliable, and cost-effective.
Another trend in flexible electronics is towards the integration of sensors and other components directly onto the flexible circuit board.
This integration allows for more compact and streamlined designs that can improve the performance and functionality of electronic devices.
By combining sensors, antennas, and other components onto a single flexible PCB, designers can create more advanced and versatile products that can meet the demands of modern technology.
In conclusion, flex PCBs and rigid flex PCBs are both important components of the growing field of flexible electronics.
While each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, both offer unique benefits that can be leveraged in a wide range of applications.
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative designs and advancements in flexible electronics that will revolutionize the way we interact with electronic devices.
